托福分数测试HOT
托福课程优惠HOT
托福正价课试听0元
新托福机考练习NEW
0元讲座HOT
新版托福入门课程HOT
托福入门导学NEW
4000人报
托福机经
PDF版
TPO练习
官方授权
资料下载
826套
专业测评
40118人已测
高分经验
1193帖

扫码免费领资料
托福全科备考资料
免费水平测试及规划

扫码关注掌握一手留学资讯
回复XDF免费水平测试
Petroleum has a lower density than the water that occupies pores, voids, and cracks in the source rock and the overlying rock and sediment layers. This density difference forces the generated petroleum to migrate upwards by buoyancy until sealed reservoirs in the proper configurations serve as traps that concentrate and collect the petroleum. Some of the generated natural gas may not migrate out and away from its source rock, but instead remains within microscopic pores and dissolved in the organic matter of its source rock. This retained natural gas has proven to be an economically significant resource that is referred to as shale gas. The Barnett Shale in the Fort Worth basin of Texas is a good example of this type of accumulation.
In some basins, petroleum may not encounter a trap and continue migrating upward into the overlying water or atmosphere as petroleum seeps. Crude oil that migrates to or near the surface of a basin will lose a considerable amount of its hydrocarbons to evaporation, water washing, and microbial degradation leaving a residual tar enriched in large complex hydrocarbons and asphaltenes (Figure 5). Tar deposits range in size from small local seeps like the La Brea tar pits of California to regionally extensive occurrences as observed in the Athabasca tar sands of Alberta.
Figure 4: Continued burial of sediment and
rock layers in subsiding basin.
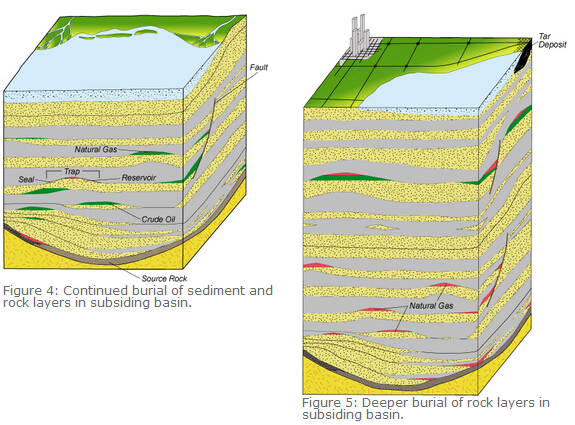
Figure 5: Deeper burial of rock layers in
subsiding basin.
Burial of the source rock may continue to depths greater than 20,000 ft. (6100 m) in some sedimentary basins. At these depths, temperatures in greater than 350ºF (177ºC) and pressures greater than 15,000 psi (103 MPa) transform the remaining organic matter into more natural gas and a residual carbon referred to as char. Oil trapped in reservoirs that are sometimes buried to these depths also decomposes to natural gas and char. The char, which is also called pyrobitumen, remains in the original reservoir while the generated natural gas may migrate upward to shallower traps within the overlying rock layers of the basin. The Gulf Coast basin that extends into the offshore of Louisiana and the Anadarko basin of the US mid-continent are good examples of these deep basins.

 资料下载
资料下载
2021-2025托福机经试题|答案|范文下载
发布时间:2024-02-21关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
托福全科备考资料大礼包
发布时间:2024-02-21关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
托福正价课试听课程包
发布时间:2024-02-21关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
托福定制备考规划
发布时间:2024-02-21关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
托福TPO免费模考
发布时间:2024-02-21关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
托福免费水平测试
发布时间:2024-02-21关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
托福写作新题型模拟题+范文汇总[ETS发布]
发布时间:2023-07-30关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
2023全年托福机经PDF版下载
发布时间:2023-06-17关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
2022全年托福机经PDF版下载
发布时间:2023-06-17关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
2022全年写作托福机经整理
发布时间:2023-01-13关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
2022年托福考后题目回忆
发布时间:2023-01-13关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
托福口语黄金80题附录音
发布时间:2023-01-13关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
新东方IBT写作网络课堂录音[.rar]
发布时间:2023-01-13关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
21天托福听力提升计划
发布时间:2023-01-13关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
不怕跑题偏题,这份写作资料请收好
发布时间:2023-01-13关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
托福阅读提分技巧锦囊妙计
发布时间:2023-01-13关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
口语拖后腿?因为你缺少这套万能句式资料
发布时间:2019-11-01关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
攻破托福听力难关的资料包
发布时间:2023-01-13关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
看剧学英语,经典美剧一键获取
发布时间:2019-11-01关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
原版外刊资源合集|精心打包整理
发布时间:2019-11-01关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取

关注新东方在线托福,
回复【XDF】获取大礼包

 推荐阅读
推荐阅读
托福考试网整理了2024托福考试时间、托福考试内容、托福写作新题型样题+范文、托福考题等内容,今天带来的是ETS官方托福阅读模拟题【2】,希望对同学们托福考试有所帮助!
托福考试网整理了2024托福考试时间、托福考试内容、托福写作新题型样题+范文、托福考题等内容,今天带来的是ETS官方托福阅读模拟题【1】,希望对同学们托福考试有所帮助!
托福考试网为大家整理了2024年托福阅读评分标准、托福阅读考试时间、托福阅读备考攻略等内容,今天给大家带来的是2024年1月托福考试考前刷题:阅读题(4),供大家参考!
托福考试网为大家整理了2024年托福阅读评分标准、托福阅读考试时间、托福阅读备考攻略等内容,今天给大家带来的是2024年1月托福考试考前刷题:阅读题(3),供大家参考!
托福考试网为大家整理了2024年托福阅读评分标准、托福阅读考试时间、托福阅读备考攻略等内容,今天给大家带来的是2024年1月托福考试考前刷题:阅读题(2),供大家参考!



 资料下载
资料下载
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取
关注新东方在线托福
回复【XDF】获取

 阅读排行榜
阅读排行榜
 相关内容
相关内容